The Critical Role of Gradeability in Rough Terrain Telehandler Performance
2025-07-22 05:25:24
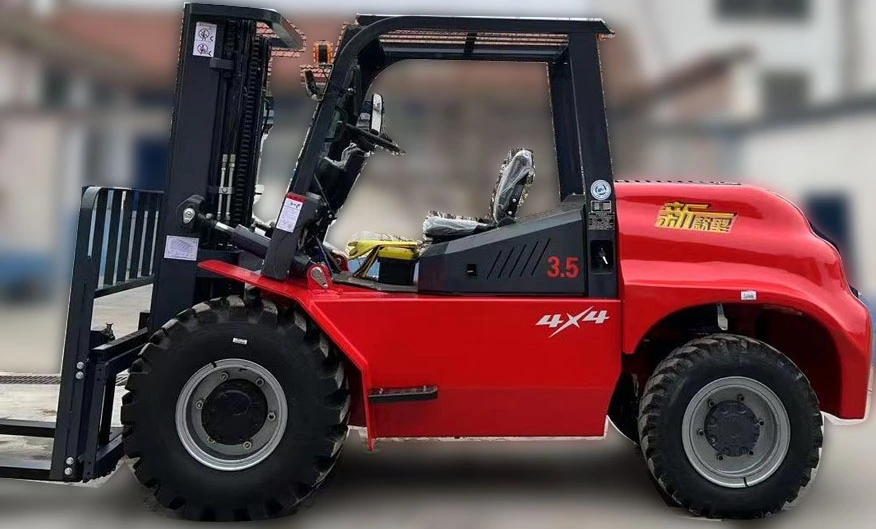
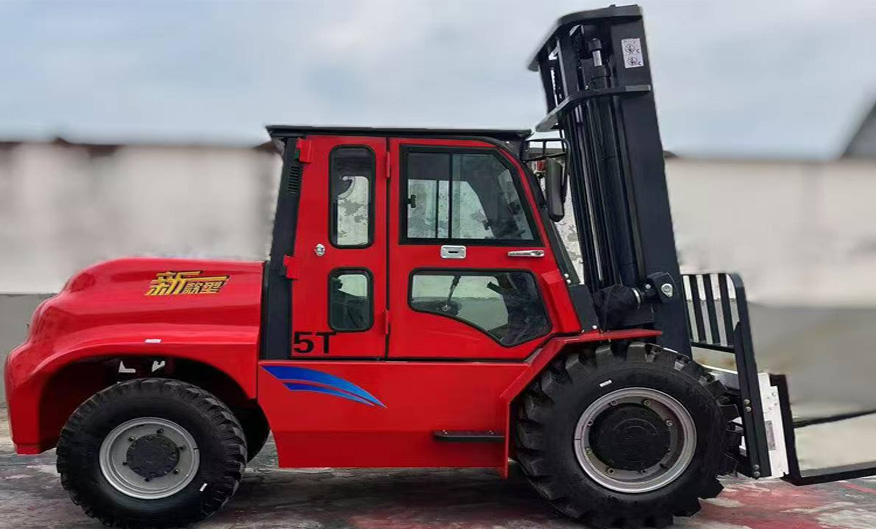
The gradeability of rough terrain telehandlers is a defining factor in their operational effectiveness, particularly in construction, agriculture, and mining sectors. Gradeability, or slope climbing capability, determines the maximum incline a telehandler can ascend or descend while maintaining stability and power. For rough terrain models, this metric is crucial due to the unpredictable and uneven surfaces they encounter. Industry data indicates that top-performing telehandlers achieve a gradeability of up to 45%, ensuring reliable performance on steep slopes.
Modern rough terrain telehandlers integrate advanced drivetrain systems to optimize gradeability. Features such as all-wheel drive, differential locks, and high-torque engines contribute to superior slope-climbing performance. According to a 2023 industry report, telehandlers with hydrostatic transmissions demonstrate a 15% improvement in gradeability compared to traditional mechanical systems. This enhancement is critical for operators navigating muddy, rocky, or uneven terrain where traction loss can lead to hazardous situations.
Safety protocols must align with a telehandler’s gradeability specifications. OSHA guidelines emphasize load management on inclines, as exceeding recommended slope limits can result in tip-overs. For instance, a rough terrain telehandler rated for 35% gradeability should not operate beyond this threshold when carrying maximum loads. Real-world accident data from 2022 shows that 22% of telehandler-related incidents occurred due to improper slope navigation, underscoring the need for rigorous operator training and adherence to manufacturer specifications.
Future advancements in rough terrain telehandler design will likely focus on enhancing gradeability through electrification and AI-driven stability control. Prototypes with hybrid powertrains have shown promise, offering instant torque delivery for improved slope performance. As industries demand greater versatility, manufacturers must continue refining gradeability metrics to meet evolving operational challenges.