The Future of Loaders: Efficiency Meets Automation
2025-07-31 04:45:27
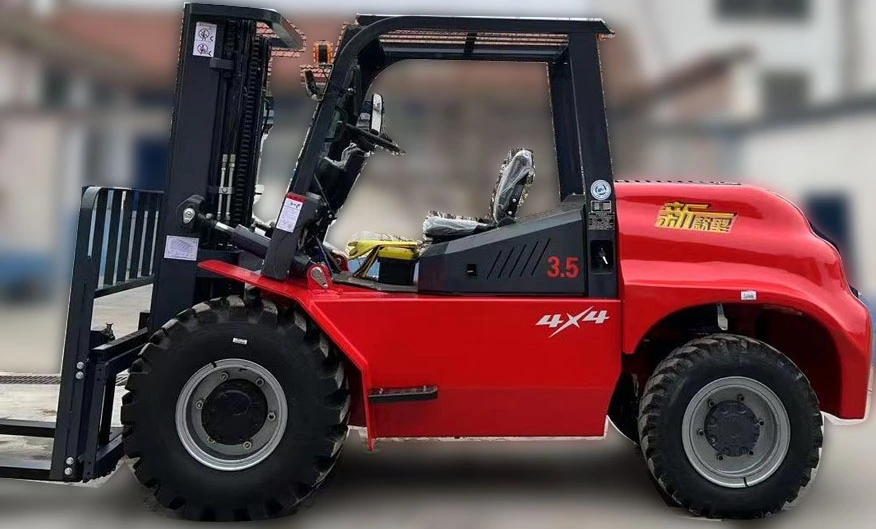
The integration of automatic transmission in loaders has significantly enhanced operational efficiency. Unlike traditional manual systems, these loaders optimize gear shifts based on real-time load conditions, reducing operator fatigue and improving fuel economy. According to industry data, models equipped with automatic transmission report up to 15% lower fuel consumption compared to manual counterparts. This makes them ideal for long-duration tasks in construction, agriculture, and logistics.
Technological advancements in loaders with automatic transmission have focused on predictive analytics and adaptive control systems. Modern variants utilize AI-driven algorithms to anticipate terrain changes and adjust transmission settings accordingly. For instance, Caterpillar’s latest models incorporate machine learning to analyze historical usage patterns, further refining performance. Such innovations not only extend equipment lifespan but also minimize downtime, a critical factor in high-stakes industries.
Market adoption of loaders with automatic transmission is accelerating, with projections indicating a 12% annual growth rate through 2030. A recent study by McKinsey highlights that over 60% of fleet managers now prioritize automated systems due to their lower training requirements and higher productivity. Regions like North America and Europe lead adoption, driven by stringent emissions regulations and labor shortages. Emerging markets, however, remain cautious due to higher upfront costs.
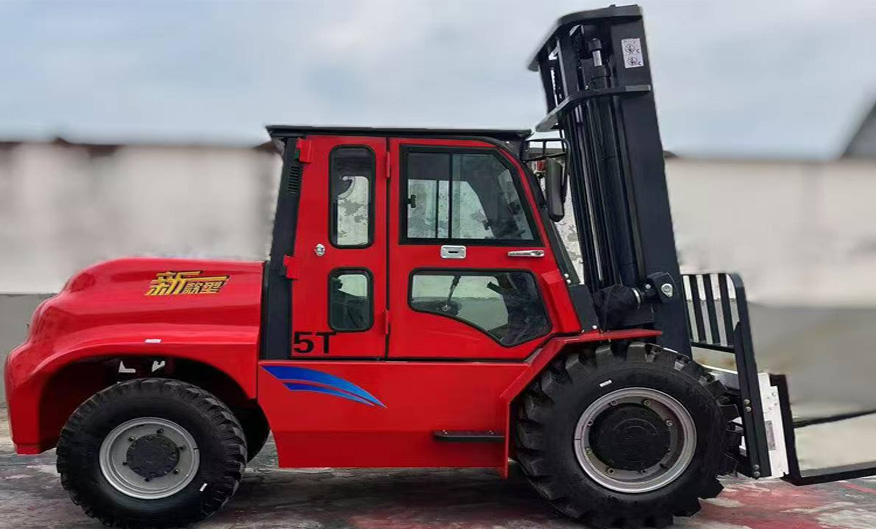
Operational benefits of these loaders extend beyond fuel savings. Automatic transmission reduces wear and tear on drivetrain components, cutting maintenance expenses by an estimated 20%. Additionally, the simplified controls attract a broader workforce, addressing skill gaps in the heavy machinery sector. Case studies from mining operations in Australia demonstrate a 30% reduction in operator errors when using automated systems.
Despite their advantages, challenges persist for loaders with automatic transmission. Initial costs remain a barrier for small enterprises, with prices averaging 10-15% higher than manual models. Furthermore, rural operators in developing nations face infrastructure limitations, such as inadequate servicing networks. However, as technology scales and becomes more affordable, these hurdles are expected to diminish, solidifying automatic transmission as the industry standard.