Navigating the Complexities of Rough Terrain Forklift Safety Regulations
2025-08-09 03:20:30
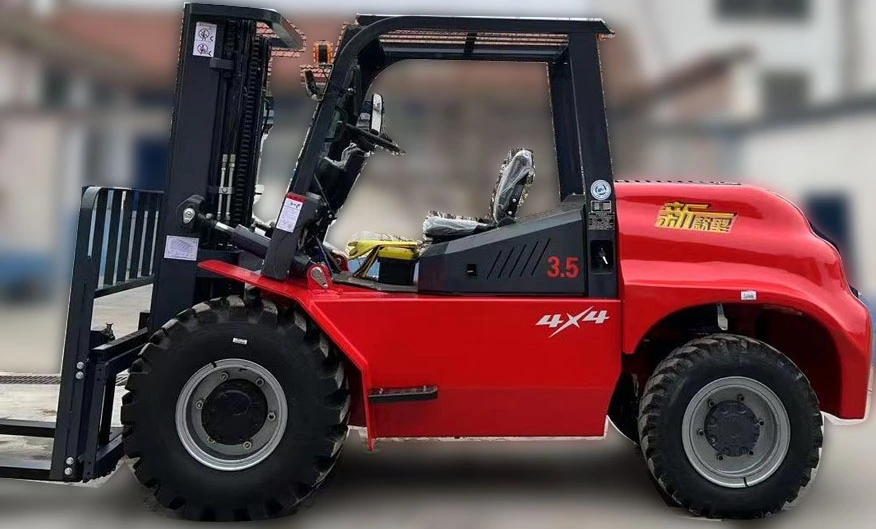
The operation of Rough Terrain Forklifts presents unique challenges due to their use in uneven, unstable, or debris-laden environments. Regulatory bodies such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute) have established stringent guidelines to mitigate risks associated with these machines. Compliance with rough terrain forklift safety regulations is not optional—it is a legal and ethical obligation for employers and operators alike.
One of the primary requirements under rough terrain forklift safety regulations is operator certification. OSHA mandates that all operators undergo formal training and evaluation before handling these vehicles. The training must cover load capacity limits, stability principles, and site-specific hazards. Studies indicate that certified operators reduce accident rates by up to 30%, underscoring the importance of adherence to these standards.
Another critical aspect of rough terrain forklift safety regulations involves regular equipment inspections. Forklifts must be examined daily for mechanical defects, tire integrity, and hydraulic system functionality. ANSI/ITSDF B56.6-2021 outlines detailed inspection protocols, emphasizing the need for documented checks. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including fines exceeding $13,000 per violation.
Technological advancements are also reshaping rough terrain forklift safety regulations. Modern forklifts now incorporate stability control systems, telematics for real-time monitoring, and automatic shutdown features in hazardous conditions. These innovations align with regulatory expectations while improving operational safety. Industry data shows that companies adopting such technologies report a 25% reduction in workplace incidents.
In conclusion, rough terrain forklift safety regulations serve as a cornerstone for accident prevention and operational excellence. By prioritizing certification, inspections, and technological integration, businesses can foster safer work environments while maintaining regulatory compliance. Continuous education and proactive risk management remain essential in this evolving landscape.