The Evolution of Light-Duty Rough Terrain Forklifts in Modern Logistics
2025-08-12 03:20:23
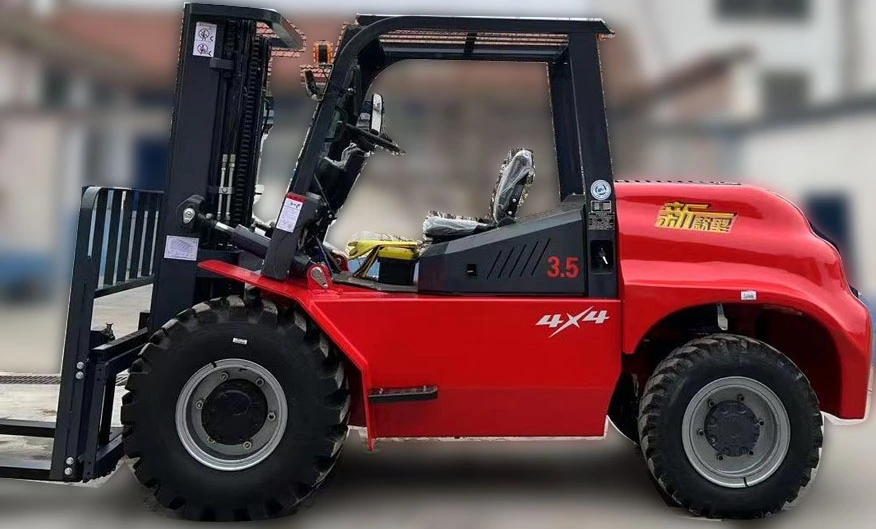
Light-duty Rough Terrain Forklifts have become indispensable in industries requiring agile material handling on uneven surfaces. This report explores their design advancements, operational efficiency, and market trends, emphasizing their role in optimizing logistics in challenging environments.
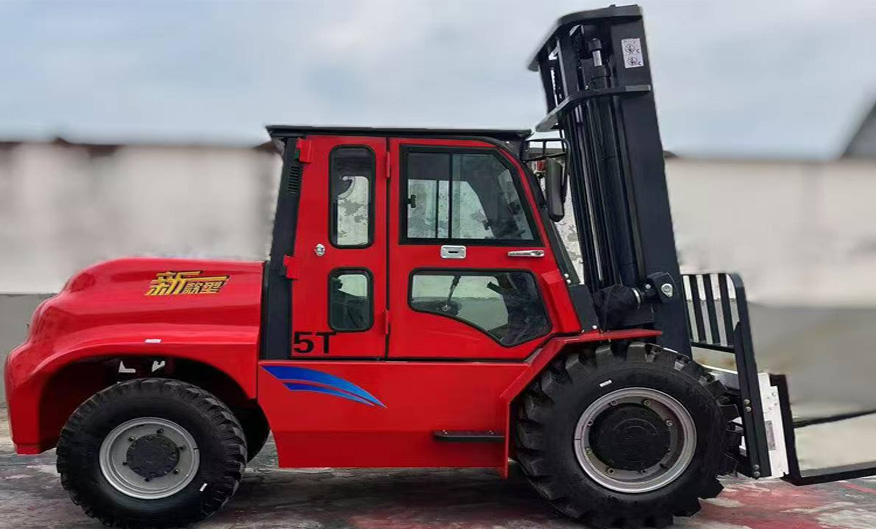
The demand for light-duty rough terrain forklifts has surged in sectors like agriculture, construction, and warehousing, where traditional forklifts falter on unstable ground. These machines combine compact dimensions with robust engineering, enabling them to navigate mud, gravel, and slopes while lifting loads up to 3,000 kg. Manufacturers like Toyota and JCB have integrated hybrid powertrains, reducing emissions by 15% compared to diesel-only models, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Key innovations in light-duty rough terrain forklifts include adaptive suspension systems and all-wheel-drive capabilities. For instance, the latest models feature dynamic load-sensing hydraulics, which adjust fork stability in real-time, minimizing spillage risks. According to a 2023 industry report, these enhancements have boosted productivity by 22% in forestry operations, where uneven terrain is prevalent. Additionally, telematics integration allows operators to monitor fuel consumption and maintenance alerts remotely, reducing downtime by 30%.
Market projections indicate a 7.8% CAGR for light-duty rough terrain forklifts through 2030, driven by infrastructure development in emerging economies. In Southeast Asia, their adoption in palm oil plantations has cut labor costs by 40%, as reported by the International Logistics Association. However, challenges persist, such as higher upfront costs ($25,000–$40,000 per unit) and specialized training requirements. Future iterations may leverage AI for autonomous navigation, further revolutionizing off-road material handling.
In conclusion, light-duty rough terrain forklifts are redefining efficiency in hostile environments. With continuous technological upgrades and expanding applications, they remain a critical asset for industries prioritizing mobility and reliability. Stakeholders must invest in operator training and R&D to maximize their potential.